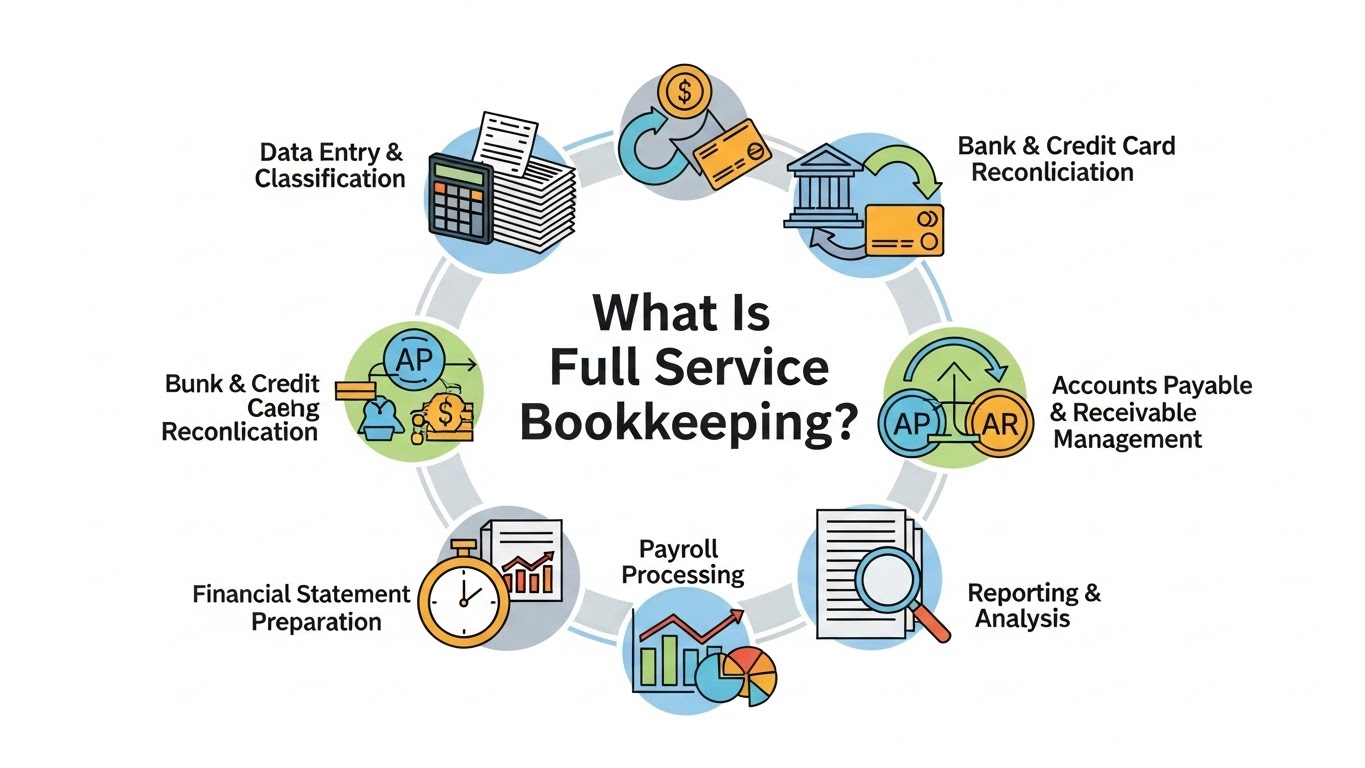
Bookkeeping is the administrative and financial process of systematically recording all business transactions into organised accounts.
It involves categorising financial data, reconciling accounts, and maintaining accurate records that support reporting, tax filing, compliance, audits, and informed decision-making.
Entities Related to Bookkeeping:
- Transactions
- General Ledger (GL)
- Chart of Accounts (COA)
- Bank Reconciliation
- Journals
- Accounts Payable (A/P)
- Accounts Receivable (A/R)
- Financial Statements
- Bookkeeper / Certified Bookkeeper
Why Bookkeeping Matters
Key reasons it’s essential:
- Ensures financial accuracy
- Helps track cash flow
- Enables tax compliance
- Supports audits
- Simplifies budgeting and forecasting
- Protects against fraud and errors
- Provides the data needed for strategic decisions
Without bookkeeping, a business operates blindly.
Key Bookkeeping Tasks
Daily/Weekly Tasks
- Recording sales invoices
- Recording expenses and supplier bills
- Managing receipts
- Reconciling cash registers and bank feeds
Monthly Tasks
- Bank and credit card reconciliation
- Preparing monthly reports
- Updating the general ledger
- Processing payroll data
Annual Tasks
- Preparing records for tax filing
- Reviewing year-end adjustments
Single-Entry vs. Double Entry Bookkeeping
Single Entry Bookkeeping
- Records each transaction once
- Suitable for small and simple businesses
- No formal ledger structure
- Limited accuracy
Double Entry Bookkeeping
- Records each transaction twice (debit & credit)
- Mandatory for GAAP and IFRS compliance
- Used by all serious businesses
- Ensures accuracy through self-balancing books
Example:
A business buys equipment for $1,000.
- Debit: Equipment
- Credit: Cash
Double-entry provides a holistic view of financial health.
Cash vs. Accrual Bookkeeping
Cash Basis
- Simple and easy
Accrual Basis
- Required for most growing businesses
- Provides a more accurate financial picture
Bookkeeping Systems and Software
Modern bookkeeping uses digital tools that automate data entry and reduce manual errors.
Popular bookkeeping software:
- QuickBooks Online
- Xero
- FreshBooks
- Wave Accounting
- Zoho Books
- Sage
These tools integrate banking feeds, invoicing, payroll, and financial reporting.
7. Core Bookkeeping Documents
A professional bookkeeping system maintains:
- General Ledger
- Trial Balance
- Journals (sales journal, purchase journal, cash book)
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Bank Statements
- Expense Receipts
- Invoice Records
- Payroll Records
These documents form the foundation of all accounting processes.
Bookkeeping vs. Accounting: What’s the Difference?
Bookkeeping
- Records and organises financial data
- Day-to-day process
- Transaction-focused
- Admin-based role
Accounting
- Interprets and analyses bookkeeping data
- Creates financial statements
- Handles audits, tax strategy, and forecasting
- Advisory role
Bookkeeping = Data Input
Accounting = Data Interpretation
Who Performs Bookkeeping?
Options include:
- In-house bookkeeper
- Freelance bookkeeper
- Virtual bookkeeping services
- Accounting firms
- Automated bookkeeping systems
- CB (Certified Bookkeeper)
- CPB (Certified Professional Bookkeeper)
The Bookkeeping Cycle Explained
The bookkeeping cycle includes:
- Identifying transactions
- Recording in journals
- Posting to the general ledger
- Balancing accounts
- Preparing trial balance
- Making adjusting entries
- Generating financial statements
- Closing the books
This cycle repeats monthly, quarterly, and annually.
Benefits of Professional Bookkeeping
Business benefits:
- Accurate financial reporting
- Better budgeting and planning
- Stress-free tax preparation
- Higher business valuation
- Strong financial governance
Operational benefits:
- Saves time
- Reduces errors
- Improves compliance
- Enhances decision-making
Common Bookkeeping Mistakes
Avoid these frequent errors:
- Mixing personal and business finances
- Missing receipts
- Ignoring bank reconciliation
- Categorising expenses incorrectly
- Not backing up financial data
Proper bookkeeping prevents these expensive mistakes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly does a bookkeeper do?
A bookkeeper records financial transactions, categorises them, reconciles accounts, manages payroll data, and prepares reports.
Is bookkeeping the same as accounting?
No. Bookkeeping records data; accounting interprets it.
Do small businesses need bookkeeping?
Yes. Even micro-businesses need accurate books for taxes, compliance, and cash-flow management.
How much does bookkeeping cost?
Costs vary based on transaction volume, business size, and service type (in-house, outsourced, or remote).
What skills does a bookkeeper need?
Attention to detail, accounting knowledge, software proficiency, reconciliation skills, and financial literacy.